The recent revolution in digital technology and cyber-physical systems has the potential to reduce costs and overcome barriers to energy efficiency, through advanced control and operation of building HVAC systems. Emerging digital tools include
- The Internet of Things (IoT); providing access to more-diverse, low-cost data on the status and activity of equipment and people in buildings.
- Artificial intelligence and data analytics; enabling more comprehensive energy performance assessment, and predictive management of assets.
- Sharing economy platforms; providing new business models for connecting users and providers of energy efficiency software services.
Unfortunately progress in the digitalization of building services has been slow, and the application of digitalization for improving energy efficiency in buildings has not reached its full potential. Open data concepts have been proposed as a way of reducing barriers and stimulating innovation in energy efficiency software services.
This project imagines a future world empowered by access to low-cost information-rich data from buildings, through an open data-exchange platform, enabling software ‘Applications’ (such as model predictive control (MPC) and fault detection and diagnosis (FDD)) to rapidly scale (see Figure below).
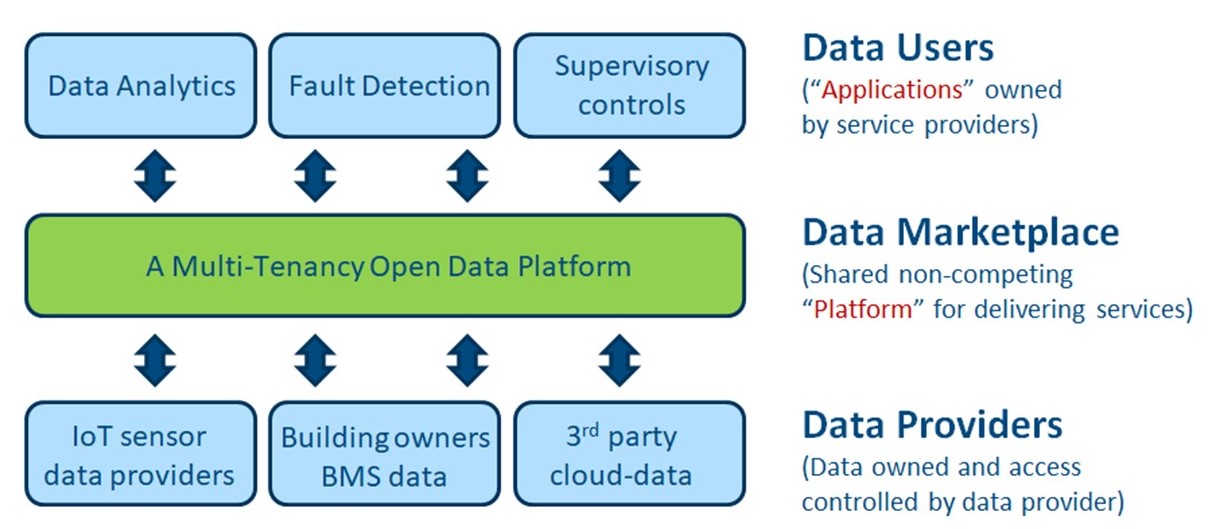
The project is divided into 4 Subtasks
- Subtask A aims to develop the knowledge, standards, protocols and procedures for low-cost high-quality data capture, sharing and utilization in buildings. It will investigate open data concepts, data governance, data platforms and data information models for building services applications
- Subtask B aims to develop develop a roadmap for scaling the use of data-driven model-based predictive control in buildings, including tools for testing and implementing MPC, and methodologies for developing MPC algorithms
- Subtask C aims to develop building energy efficiency (and related) ‘applications’ that can be used (and ideally commercialized) for reducing energy consumption in buildings and coordinating building energy demand to achieve additional electricity system benefits.
- Subtask D will drive adoption of Annex results through case studies, business model innovation and results dissemination
The planned deliverables from this project are:
- functional-requirements for an MVP Open Data Platform;
- an online repository of exemplar data-sets for building analytics research;
- a set of data-driven control-oriented building models for different scenarios;
- a software repository, containing prototype software implementations and Application descriptions;
- a data-driven Applications grand challenge
- a proposal for government leadership on data sharing from their buildings;
- subtask reports
Participants: Australia, Austria, Belgium, Canada, China, Denmark, Finland, Ireland, Italy, Japan, Netherlands, Norway, Singapore, Spain, Sweden, Turkey, United Kingdom, United States of America